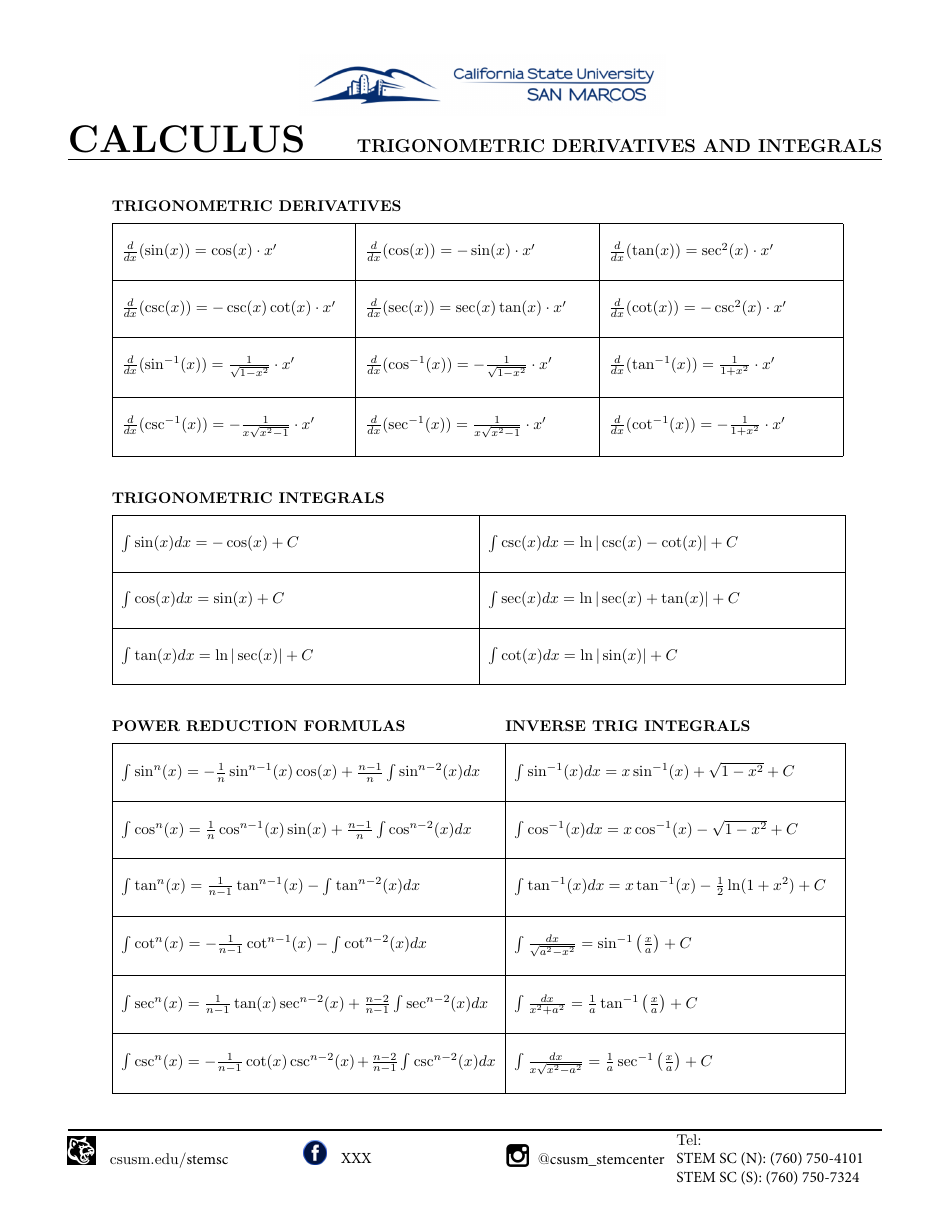
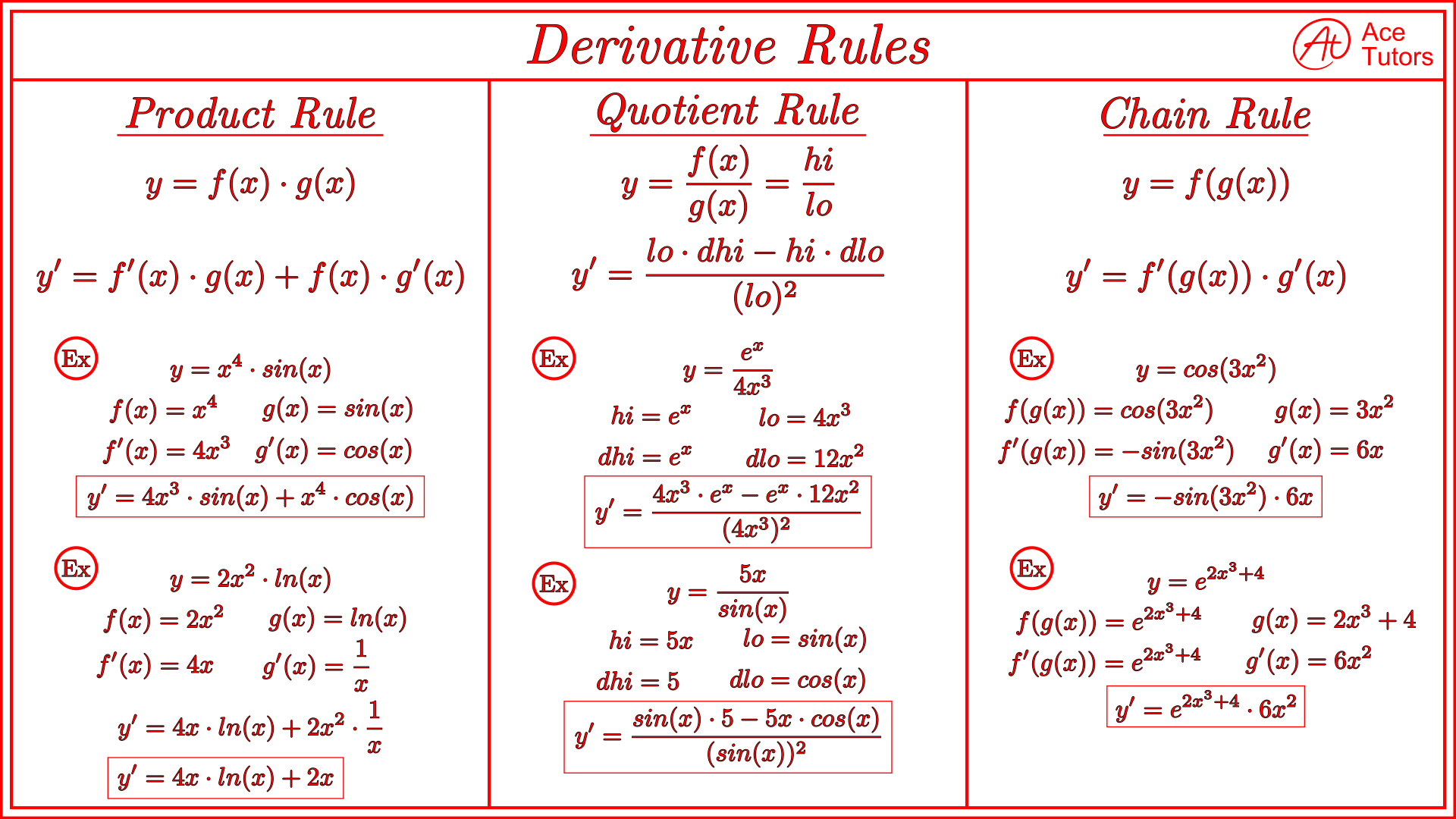
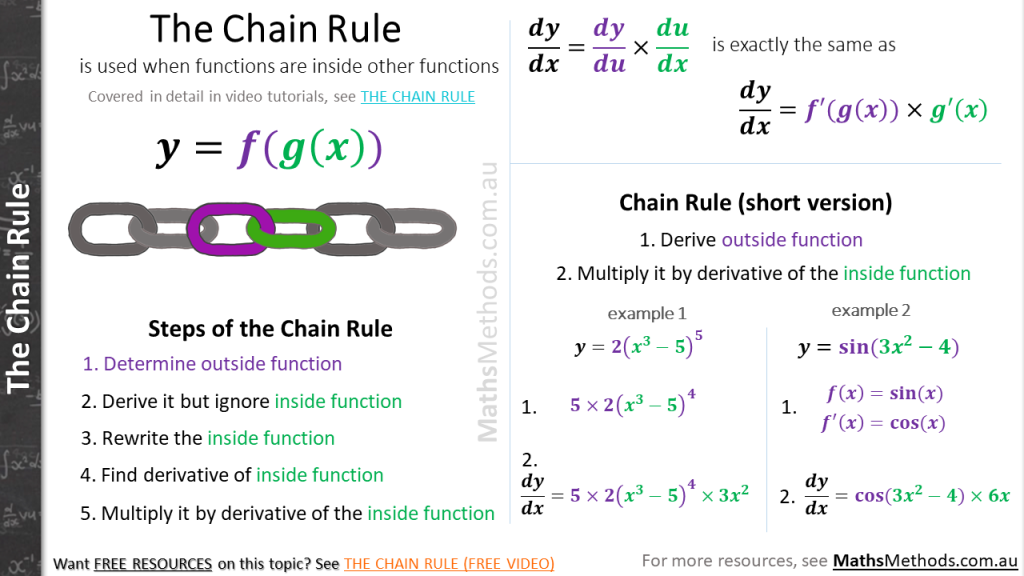
Calculus Derivative Cheat Sheet - Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Add on a derivative every time. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga (x)) = 1 xln (a)
Add on a derivative every time. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga (x)) = 1 xln (a)
Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga (x)) = 1 xln (a) The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Add on a derivative every time. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e.
Trigonometric Derivatives and Integrals Calculus Cheat Sheet Download
Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga (x)) = 1 xln (a) Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Add on a derivative every time..
Derivative Cheat Sheet DERIVATIVE CHEAT SHEET YouTube
Add on a derivative every time. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function..
Calculus Cheat Sheet Derivatives Download Printable PDF Templateroller
The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)).
Derivative Rules Cheat Sheet Calculus Ace Tutors Blog
The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule.
Derivative Cheat Sheet
Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. Add on a derivative every time. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function..
SOLUTION Derivatives and Integral Calculus Study Guide Cheat
Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule.
Calculus Derivative Cheat Sheet Johns Hopkins University Edubirdie
Add on a derivative every time. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (|.
Derivative calculus Cheat Sheet Etsy
The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga.
SOLUTION Calculus derivative cheat sheet Studypool
Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and y will use the product/quotient rule and derivatives of y will use the chain rule. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1.
Derivative Cheat Sheet DERIVATIVE CHEAT SHEET YouTube
Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e. Add on a derivative every time. The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Remember y = y ( x ) here, so products/quotients of x and.
Remember Y = Y ( X ) Here, So Products/Quotients Of X And Y Will Use The Product/Quotient Rule And Derivatives Of Y Will Use The Chain Rule.
The derivative of a product of two functions is the derivative of the first function times the second function plus the derivative of the second function. Common derivatives d dx (ln (x)) = 1 x d dx (ln (| x |)) = 1 x d dx (ex) = ex d dx (log (x)) = 1 xln (10) d dx (loga (x)) = 1 xln (a) Add on a derivative every time. Write down equation relating quantities and differentiate with respect to t using implicit differentiation (i.e.