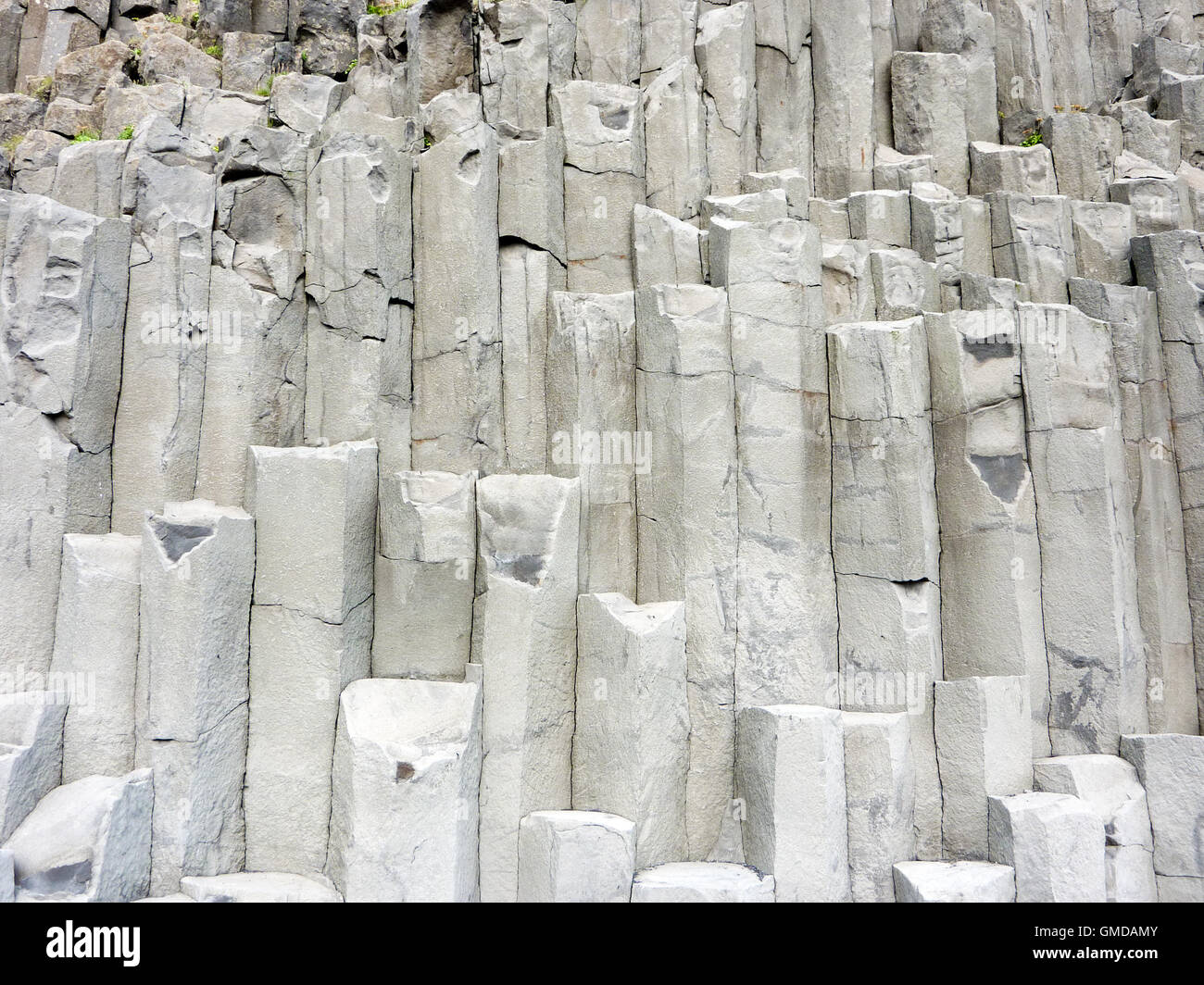
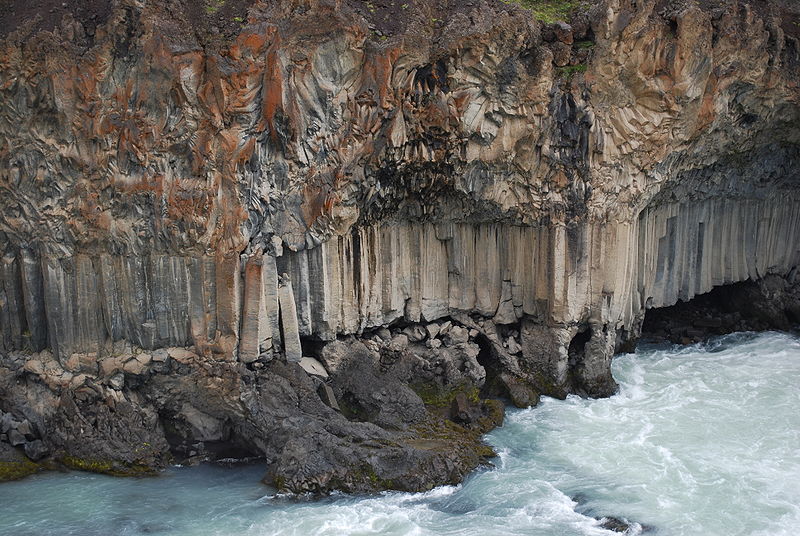
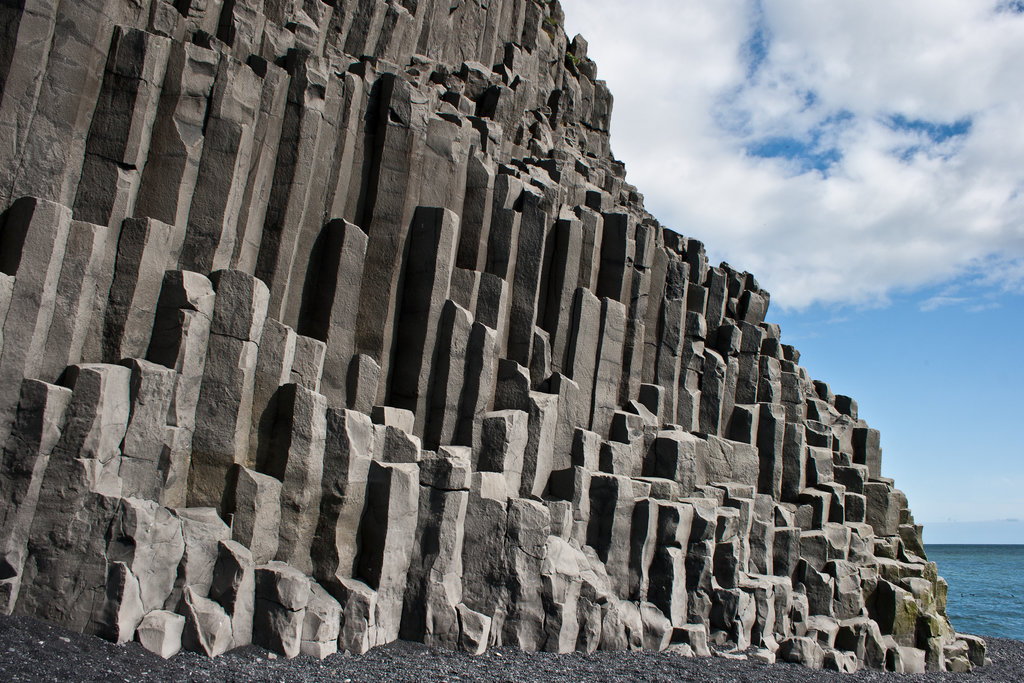
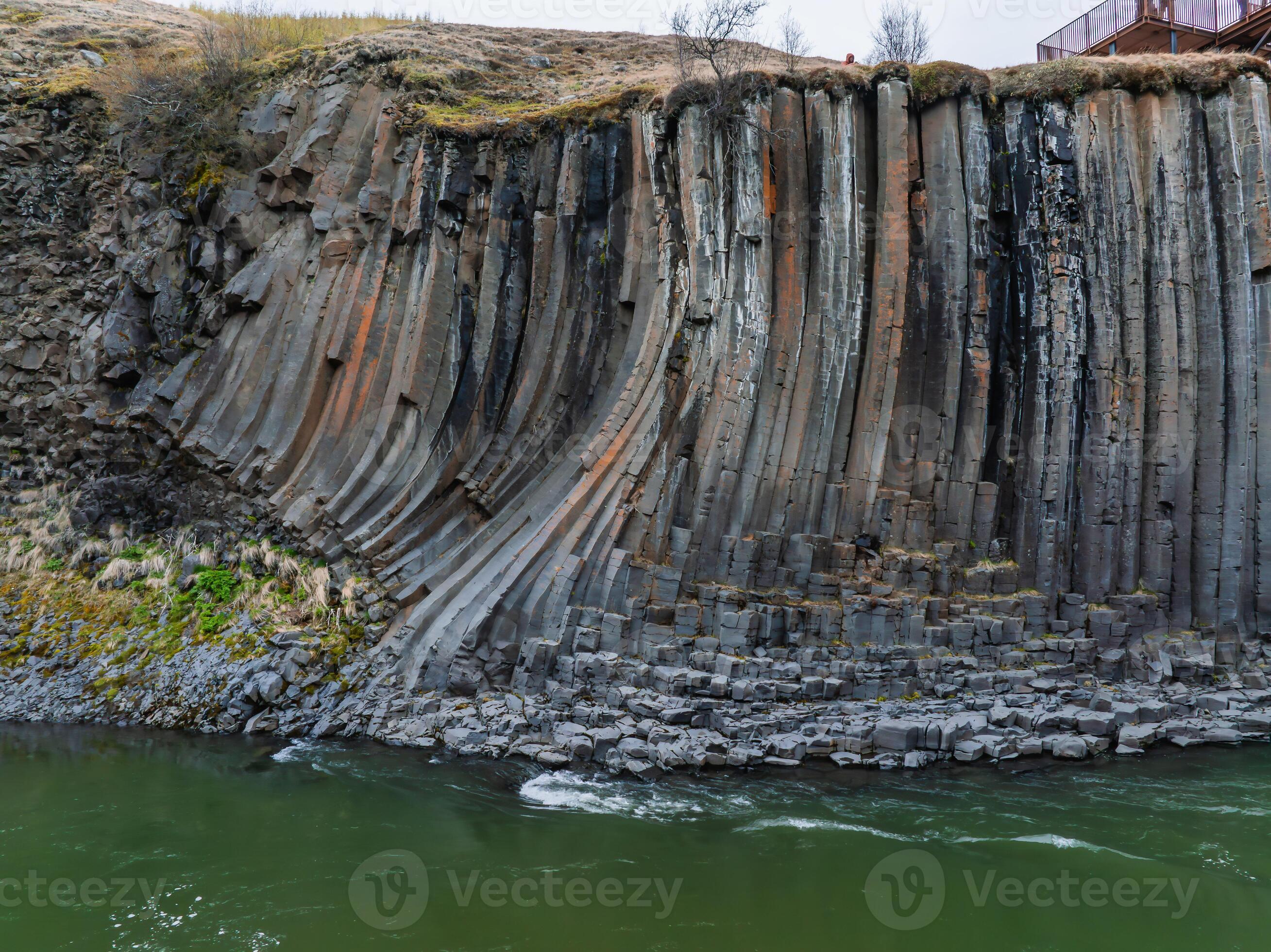
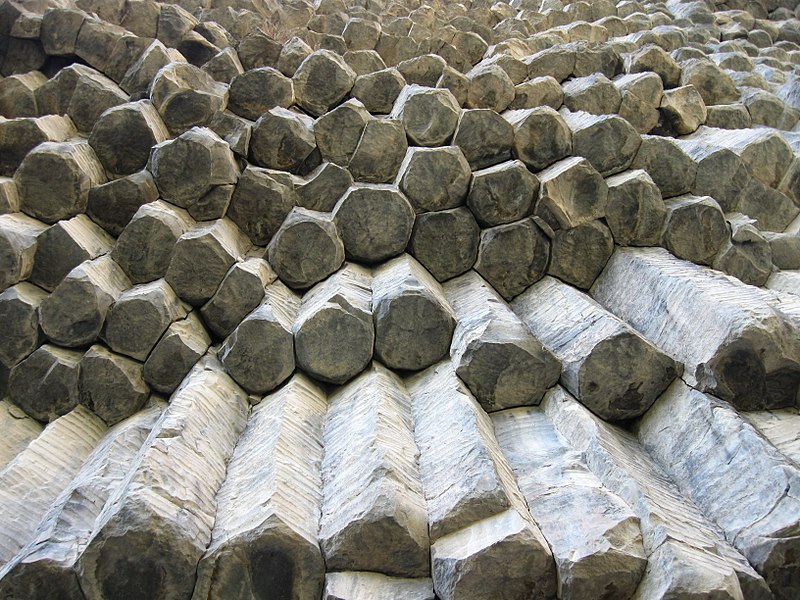
How Are Basalt Columns Formed - Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It most commonly forms as an. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava.
Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. It most commonly forms as an. Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art.
The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. It most commonly forms as an.
Tectonics and Structural Geology Features from the Field Columnar
Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. It most commonly forms as an. The shape, structure and texture of.
Columnar Basalt Rock, Cape Stolbchaty on Kunashir Island, in the
Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It most commonly forms as an. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications,.
Basalt columns and steps hires stock photography and images Alamy
The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. It most commonly forms as an. Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed.
How Are Basalt Columns Formed? Ask An Earth And Space Scientist
Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. It most commonly forms as an. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. Explore the strength and versatility of.
Columnar Basalts Form Where Lava Flows Underwater at Darcy Housley blog
Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is.
Basalt Learning Geology
Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. It most commonly forms as an. Explore the strength and versatility of.
Aerial View of Basalt Rock Formation with Vertical Columns Near Water
Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. It most commonly forms as an. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. The shape, structure and texture of.
Columnar Jointing Volcanoes, Craters & Lava Flows (U.S. National Park
It most commonly forms as an. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is formed from the solidification of molten lava. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt, extrusive.
How Are Basalt Columns Formed? Ask An Earth And Space Scientist
Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. It most commonly forms as an. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through.
Columnar Basalt Rock, Cape Stolbchaty on Kunashir Island, in the
Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. Basalt is a type of volcanic rock that is.
It Most Commonly Forms As An.
Explore the strength and versatility of basalt, a volcanic rock with widespread uses in construction, industrial applications, and art. The shape, structure and texture of a basalt is diagnostic of how and where it erupted—for example, whether into the sea, in an explosive cinder. Basalt, extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock that is low in silica content, dark in color, and comparatively rich in iron and magnesium. It is an igneous rock, meaning it is formed through the.