Infinite Fusions Rotom Forms - Series solutions of differential equations at regular points? All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. From what foundation/background are you approaching this. To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Are you familiar with taylor series? They often come with a topology and we.
From what foundation/background are you approaching this. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Are you familiar with taylor series? I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points? They often come with a topology and we.
To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. They often come with a topology and we. From what foundation/background are you approaching this. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points? Are you familiar with taylor series? I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite.
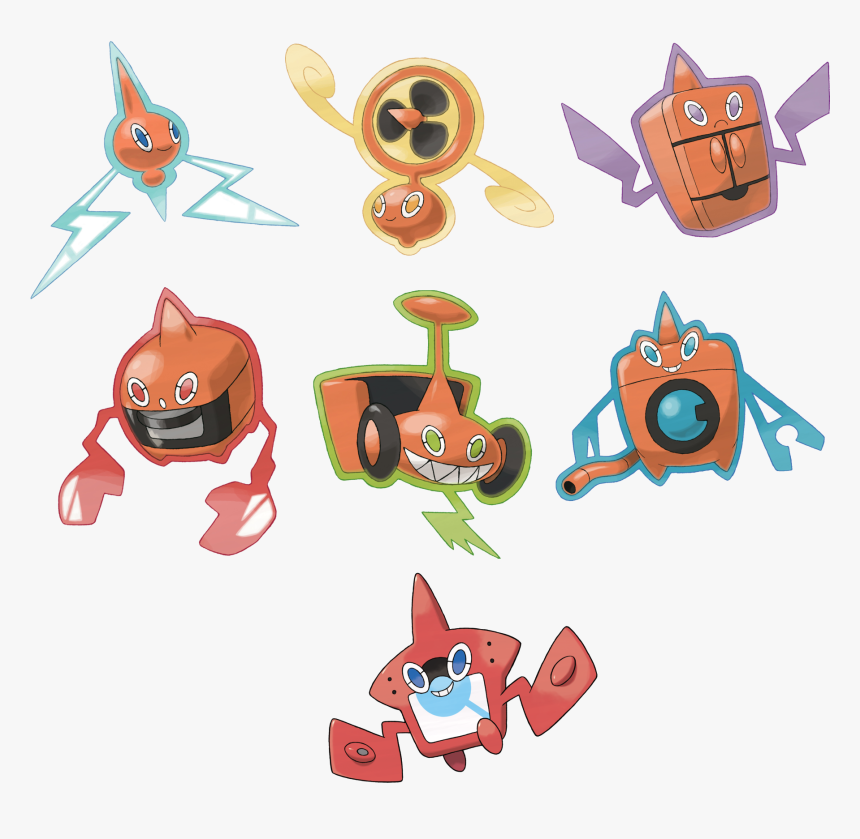
Infinite Fusions Rotom Forms
From what foundation/background are you approaching this. Are you familiar with taylor series? All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. They often come with a topology and we. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points?
Coolest Rotom Fusions Pokemon Infinite Fusion YouTube
From what foundation/background are you approaching this. I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. Are you familiar with taylor series? To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points?
Legendary Rotom Fusions Pokemon Infinite Fusion YouTube
They often come with a topology and we. Are you familiar with taylor series? I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. Series solutions of differential equations at regular.
My Viewers Found the BEST Rotom Pokemon Fusions YouTube
They often come with a topology and we. To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. From what.
Rotom Mega Evolution
To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Are you familiar with taylor series? All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. From what foundation/background are you approaching this. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points?
Rotom Rotom Forms, HD Png Download , Transparent Png Image PNGitem
To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. They often come with a topology and we. I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points? From what foundation/background are you approaching this.
Hexafusion porygon z, haunter, rotom Pokemon fusion art, Pokemon art
To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Are you familiar with taylor series? From what foundation/background are you approaching this. I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points?
Where to get Rotom in Pokemon Infinite Fusion infinitefusion YouTube
I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. From what foundation/background are you approaching this. Are you familiar with taylor series? All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. They often come with a topology and we.
Infinite Fusions Rotom Forms
I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. They often come with a topology and we. Are you familiar with taylor series? Series solutions of differential equations at regular.
A new breed of Rotom is now able to possess robotic Pokémon (There’s
I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite. Are you familiar with taylor series? They often come with a topology and we. Series solutions of differential equations at regular points? From what foundation/background are you approaching this.
They Often Come With A Topology And We.
From what foundation/background are you approaching this. All three integrals are divergent and infinite and have the regularized value zero, but two of them are equal but not equal to the third one. To provide an example, look at $\\langle 1\\rangle$ under the binary. Are you familiar with taylor series?
Series Solutions Of Differential Equations At Regular Points?
I am a little confused about how a cyclic group can be infinite.